-

-
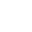
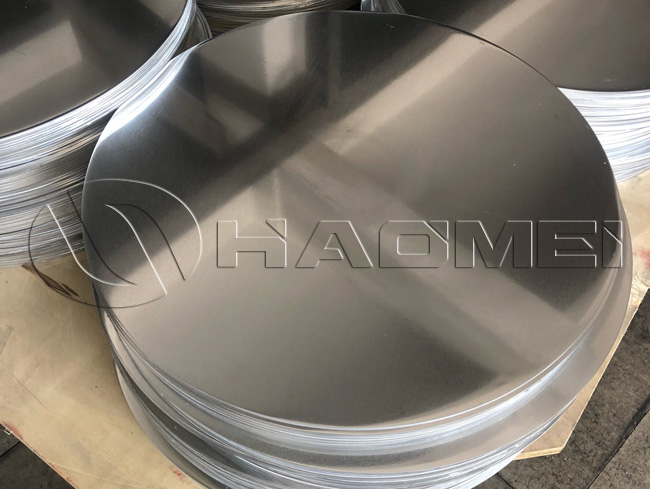
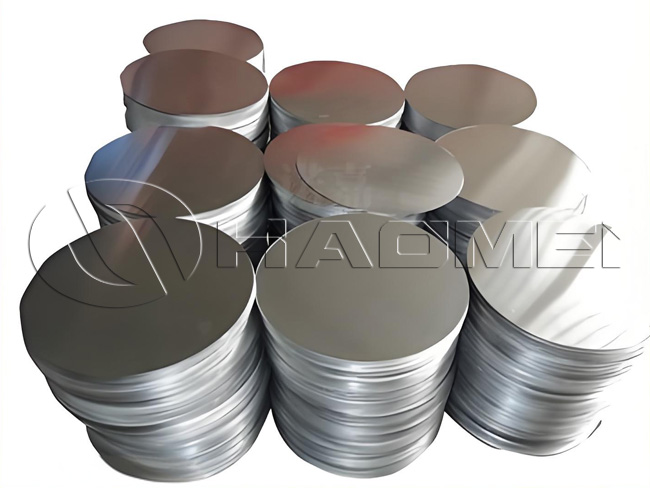
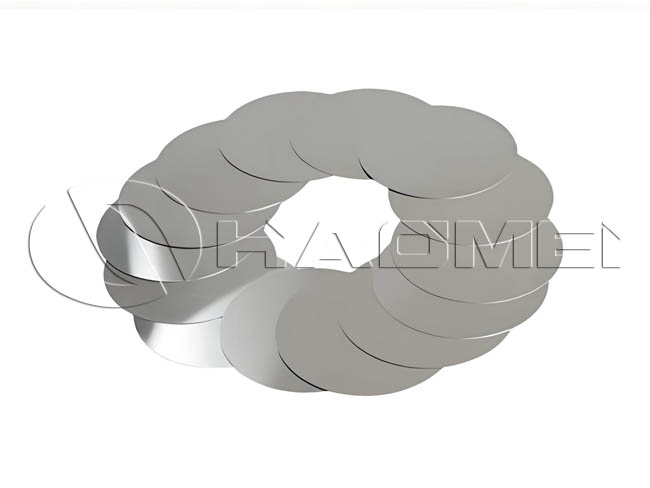
Hot Rolled Aluminum Circle
- Alloy 1050, 1060, 1070, 1100, 1200, 3003, 3004, 3105, 8011, etc.
- Temper O-H112
- Thickness 0.5 mm - 6.0 mm
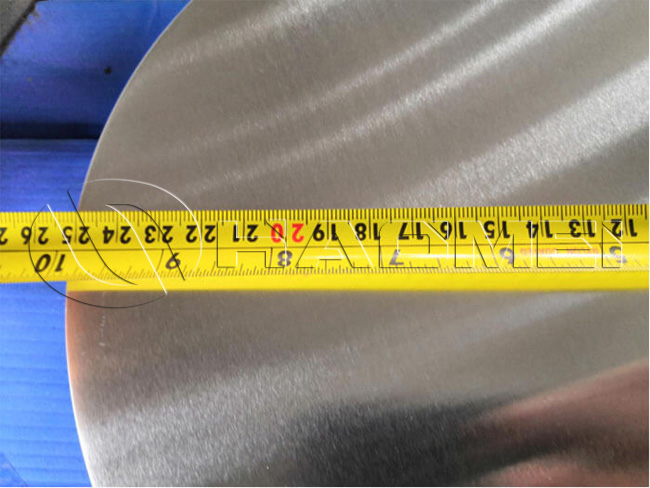
- Diameter 100 mm - 900 mm
- Applications Reflective road signs, utensils, casserole bases, cookware, etc.
- Packing Standard export wooden pallets
- MOQ 1 - 3 tons
What is a Hot Rolled Aluminum Circle?
A hot rolled aluminum circle is a round aluminum product produced through the hot rolling process. It uses aluminum alloy ingots as raw material, which are rolled into sheets at high temperature (usually above the recrystallization temperature, about 600–700℃), and then processed by cutting, stamping, or other methods into circular aluminum discs. It is a widely used basic semi-finished product in the aluminum processing industry.
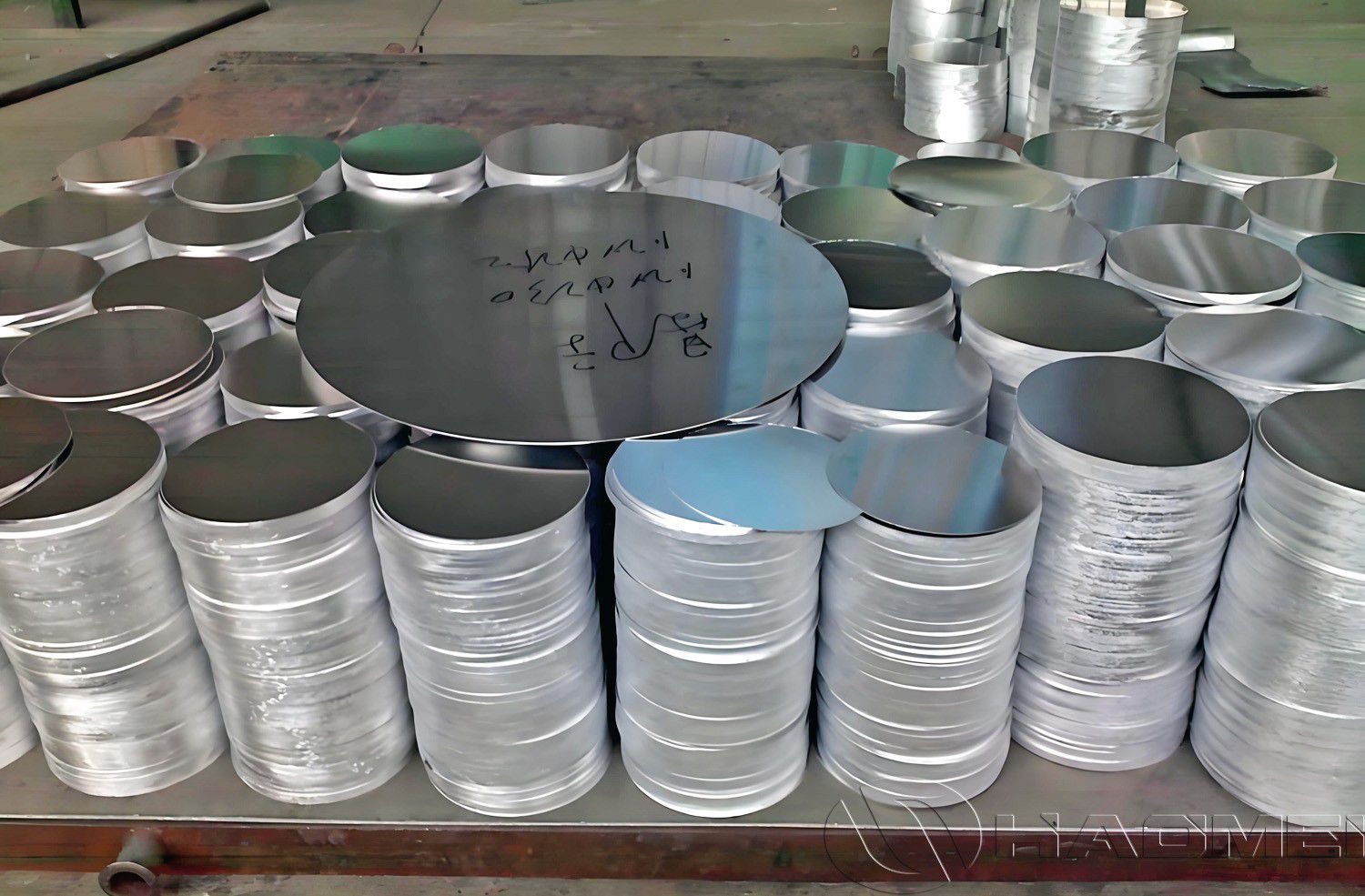

Common alloys for DC Aluminum Circle
1050 / 1060 / 1100 series: These are pure aluminum grades with high aluminum content. They have excellent plasticity and ductility, making them ideal for deep-drawing products (such as cookware). The hot rolling process further enhances their formability.
3003 series: An aluminum-manganese alloy with higher strength than pure aluminum while retaining good formability and corrosion resistance. Hot rolled 3003 aluminum circles are often used in products requiring both strength and formability, such as certain cookware and containers.
5052 series: An aluminum-magnesium alloy with medium strength and excellent corrosion resistance, especially in marine and atmospheric environments. Hot rolled5052 aluminum circles are commonly used for deep-processed products requiring higher strength and corrosion resistance, such as fuel tanks and automotive components.
8011 series: An aluminum-iron-silicon alloy known for its excellent deep-drawing performance and food safety. Hot rolled 8011 aluminum circles are widely used to produce high-quality non-stick pans, frying pans, and bottle caps.
Core Characteristics of Hot Rolled Aluminum Circles
Coarser grain structure with superior ductility
During high-temperature rolling, aluminum grains fully recrystallize, forming a looser grain structure. This makes hot rolled aluminum circles more ductile and suitable for deep deformation processes (such as stretching, spinning, or stamping into complex surfaces) without cracking.Wider thickness range and stronger load capacity
Hot rolling can directly process thick ingots, covering finished thicknesses of 1–10 mm or even thicker (cold rolling is better for thinner gauges such as 0.1–3 mm). This makes hot rolled circles suitable for applications requiring thickness and structural strength.Higher surface roughness, requiring post-treatment
During hot rolling, friction and oxidation between aluminum and rollers cause lower surface smoothness (Ra 1.6–6.3 μm). For appearance-critical applications (e.g., decorative parts), additional polishing, coating, or surface finishing is required. However, the rougher surface improves adhesion for coatings and films, which is advantageous in some cases.Cost-effective
Hot rolling requires lower initial precision of raw ingots and achieves higher rolling efficiency, making it suitable for mass production of medium and thick products at lower overall cost compared with cold rolled products of the same thickness.
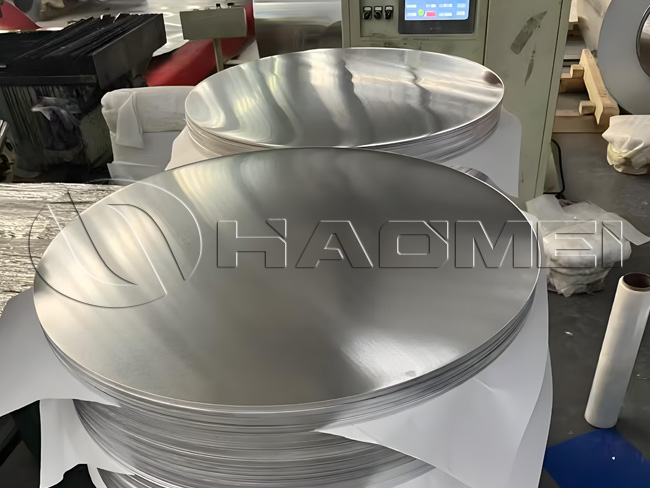
DC Aluminum Circle Product Information
| Alloy | 1050, 1060, 1070, 1100, 1200, 3003, 3004, 3105, 8011, etc. |
| Temper | O - H112 |
| Thickness | 0.5 mm - 6.0 mm |
| Diameter | 100 mm - 1200 mm |
| Surface | Mill finish, mirror polished, brushed, embossed, PE/PVDF color coated, etc. |
| Applications | Reflective road signs, utensils, casserole bases, cookware, etc. |
| Packing | Standard export wooden pallets |
| MOQ | 1-3 tons |
Applications of Hot Rolled Aluminum Circles
Thanks to their excellent deep drawing performance and strength, hot rolled aluminum circles are widely used in:
High-quality cookware: Non-stick pans, pressure cookers, frying pans, etc., where bottoms and bodies require deep drawing.
Lighting industry: For deep-drawn lampshades and lamp housings.
Traffic signs: Certain road signs requiring thickness and strength.
Industrial manufacturing: Various deeply processed industrial components.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Hot Rolled Aluminum Circles
Advantages:
Can produce thick-gauge products: Hot rolling economically produces medium/thick plates that cold rolling cannot easily achieve (e.g., thickness >6 mm).
Lower production cost: Hot rolling has lower deformation resistance, higher efficiency, and relatively lower energy consumption compared with cold rolling.
Excellent deep drawing performance: Hot rolled material usually has equiaxed grain structure and uniform internal organization, giving it outstanding deep-drawing ability in O temper, suitable for cookware and lampshades.
Isotropic mechanical properties: Hot rolled products have more uniform mechanical properties in all directions, unlike cold rolled materials which often show anisotropy.
Disadvantages:
Lower dimensional accuracy and surface finish: Due to high-temperature processing, oxide films form on the surface, and roller deflection affects thickness precision. The surface is usually dull or slightly oxidized.
Lower strength: Hot rolled materials are often annealed afterward, making them weaker compared with cold rolled products of the same gauge in hard or semi-hard tempers.

Differences Between Hot Rolled and Cold Rolled
1. Processing temperature: Hot rolling is performed at high temperature, cold rolling at room temperature.
2. Raw material and production: Hot rolling uses heated aluminum ingots, cold rolling uses cast-rolled coils directly.
3. Performance differences: Hot rolled sheets have better plasticity and are suitable for stamping, while cold rolled sheets have higher hardness and smoother surfaces, suitable for precision applications.
4. Thickness range: Hot rolling typically produces thicker sheets (6-8 mm and above), while cold rolling is better for thinner sheets (0.5-4.5 mm).

 No.14 Waihuan Road, CBD, Zhengzhou, China
No.14 Waihuan Road, CBD, Zhengzhou, China +86-18703635966
+86-18703635966 












 +86-18703635966
+86-18703635966
 sales@alummc.com
sales@alummc.com
 8618703635966
8618703635966